Blockchain Technology: How It Works and How It’s Changing Everything
Blockchain technology is ushering in a new wave of the digital revolution. First and foremost, it is the backbone of cryptocurrencies. Crypto has had a very disruptive impact on financial markets.
This relatively new asset class is being included in portfolios for some Morgan Stanley (NYSE: MS) clients. A crypto checkout feature was added to PayPal’s (Nasdaq: PYPL) services. On the other end of the spectrum, the disruptive nature of crypto has led to India considering a ban on crypto. And China has begun to roll out its own digital yuan.

As these reactionary measures are being taken, cryptocurrencies have been having one heck of a year. The meme-based Dogecoin shot up in value – seemingly out of nowhere. And new coins like Elongate and SafeMoon are enticing new crypto investors. On top of all of this, one of our favorite crypto exchanges, Coinbase (Nasdaq: COIN) is now listed on a major exchange.
It’s clear that blockchain technology has already had huge impacts since it was introduced in 2009. Back then, you could get your hands on some Bitcoin for well under a penny per coin. Now that it has ballooned in price (to more than $60,000 at times), it’s minted more than 100,000 millionaires, according to some estimates.
Blockchain technology is at the core of crypto’s success. It’s the out-in-the-open secret to how folks have been making money during the crypto revolution. Every cryptocurrency that currently exists uses blockchain technology.
But cryptocurrencies are just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to blockchain applications. This technology is poised to make the leap into everyday transactions. And the gains for early investors could be huge. But before we get to those…
A Brief History of Blockchain Technology
As we alluded to above, blockchain technology started with Bitcoin. Because you can’t physically hold Bitcoin – or any cryptocurrency for that matter – it was vital to develop a safe, secure and transparent digital ledger for every user’s account. The creators did so by developing a global distributed ledger.
This global network of unassociated computers used blockchain technology to collectively manage the database that recorded Bitcoin transactions. To break this down a little further, Bitcoin is managed by its network of individuals… not by any one central authority. This right here is the crux of cryptocurrencies’ decentralized nature. This is why so many hard-line crypto investors prefer it to traditional transactions.
Anytime someone uses a credit card, debit card, ATM card, PayPal or pretty much anything besides crypto or cash, all of the details are collected in a centralized database. This database keeps all the transactions and customer records. And that can be problematic.
Centralized databases can be, have been, and will again be hacked or breached. It wasn’t that long ago that the largest data breach ever occurred. When the Yahoo data breach happened, it affected the sensitive personal information of all 3 billion Yahoo account holders. At the time, that was just shy of half the world’s population. So it’s easy to see the problem with a centralized means of data collection.
And therein lies the beauty of blockchain technology. Because it is decentralized, a hack or breach of the system is virtually impossible. Here’s why…
A Safer Store of Information
Blockchain technology, through encryption, securely records transactions and stores them in blocks on the network of computers that has access to the blockchain. That way everyone in the network has an opportunity to verify any transaction they made.
The key word there is “they.” If you weren’t part of the transaction, you can’t tamper with it. You can modify only transactions you are involved in. And the person or persons you are transacting with must also agree to these modifications.
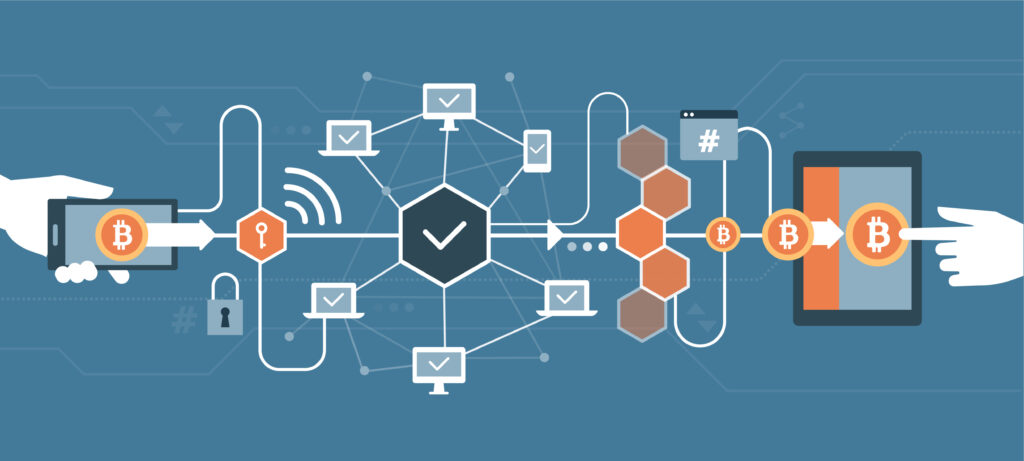
The blockchain uses encrypted keys assigned to all its individual users. Everyone involved in creating a new unit of crypto holds a copy of the blockchain. Each copy perfectly reflects all other copies. Each part of the Bitcoin network represents the whole of the Bitcoin network.
This replication process makes hacking transactions or data extremely difficult. To hack one block of information, a person would need to go through all the blocks before it in the chain.
So if your transaction is in block number 3,451, to hack that one block, a hacker would need to go through the 3,450 blocks before it. And keep in mind, the system is updated constantly. That’s one reason the Bitcoin network is so secure.
Unlike a central database or a central server, there’s no single target to attack. My computer, your computer and the thousands of others that have made transactions are the server. This is how the power and security of blockchain technology is distributed through the entire network.
From Bitcoin to Broader Adoption
The blockchain protocol – in the form of global distributed computations – ensures the integrity of the data exchanged among billions of devices. And it negates the need for a third party or centralized database.
The beauty of blockchain technology is that it can be programmed to record almost anything of value or importance. It’s a safe place to store birth and death certificates. Deeds and titles of ownership would be about as secure there as in a safe in your home. Financial accounts, voting records and medical records could and probably will be migrated onto blockchain technology.
While this is good news for much of the world, not everybody is thrilled with the disruptive possibilities of the blockchain. As more information makes its way onto blockchains, there will be less need for third-party organizations to verify and keep track of information. It’ll all be right there at our fingertips.
It’s a much simpler way to keep track of things. There will be less need for unnecessary middlemen. And everyone will have access to what they did.
This is why so many companies are so eager to apply blockchain technology to their respective businesses and industries. Big companies like Microsoft (Nasdaq: MSFT) and IBM (NYSE: IBM) are working on developing software for blockchain use. Wall Street giants like JPMorgan Chase (NYSE: JPM), Goldman Sachs (NYSE: GS) and Bank of America (NYSE: BAC) are trying out some of the technology as well.
Blockchain technology has already created an extremely trustworthy model in the financial sector it was born from. It’s led to increased transparency. It’s all but eliminated the need for regulators. It can conduct transactions cheaper and faster than traditional means can. And that’s exactly why it’s rapidly spreading far and wide.
The Bottom Line on Blockchain Technology
We’ve only begun to scratch the surface of blockchain technology’s capabilities and applications. As it branches out from the world of cryptocurrency into the more mundane, mainstream functionality, early adopters will be rewarded handsomely.
If you’re looking for ways to get in on the action, check out our list of six blockchain stocks to invest in here. But if you’d prefer to stick to crypto, we highly recommend checking out this piece explaining everything you need to know to win with digital currency. And if you like what you’ve been reading, we suggest signing up for the Manward Financial Digest e-letter below. By doing so, you’ll learn everything you need to know in order to be a successful trader.







127 Comments
[…] leaders embracing and growing leading edge blockchain applied sciences. It’s no secret that blockchain technology is poised to disrupt all kinds of industries. And this convention is internet hosting greater than […]
[…] adoptant et développant des technologies de blockchain de pointe. Ce n’est pas un secret que technologie blockchain est sur le point de perturber toutes sortes d’industries. Et cette conférence accueille plus […]
[…] leaders embracing and developing cutting edge blockchain technologies. It’s no secret that blockchain technology is poised to disrupt all sorts of industries. And this conference is hosting more than 230 speakers […]
[…] leaders embracing and developing cutting edge blockchain technologies. It’s no secret that blockchain technology is poised to disrupt all sorts of industries. And this conference is hosting more than 230 speakers […]
[…] leaders embracing and developing cutting edge blockchain technologies. It’s no secret that blockchain technology is poised to disrupt all sorts of industries. And this conference is hosting more than 230 speakers […]
[…] leaders embracing and developing cutting edge blockchain technologies. It’s no secret that blockchain technology is poised to disrupt all sorts of industries. And this conference is hosting more than 230 speakers […]
[…] leaders embracing and growing leading edge blockchain applied sciences. It’s no secret that blockchain know-how is poised to disrupt all types of industries. And this convention is internet hosting greater than […]
[…] leaders embracing and developing cutting edge blockchain technologies. It’s no secret that blockchain technology is poised to disrupt all sorts of industries. And this conference is hosting more than 230 speakers […]
[…] leaders embracing and developing cutting edge blockchain technologies. It’s no secret that blockchain technology is poised to disrupt all sorts of industries. And this conference is hosting more than 230 speakers […]
[…] record with the most important stablecoin by market cap. Tether is a reasonably commonplace blockchain-based cryptocurrency. When it first launched in 2014, Tether got down to again every token 1:1 with […]
[…] منبع:https://dev2.investmentu.com/ […]
[…] version of the internet. Already, it features applications and services that make use of blockchain technology. As such, it’s a community-owned and driven project. To date, there are more than 250 […]
[…] version of the internet. Already, it features applications and services that make use of blockchain technology. As such, it’s a community-owned and driven project. To date, there are more than 250 […]
[…] version of the internet. Already, it features applications and services that make use of blockchain technology. As such, it’s a community-owned and driven project. To date, there are more than 250 […]
[…] version of the internet. Already, it features applications and services that make use of blockchain technology. As such, it’s a community-owned and driven project. To date, there are more than 250 […]
[…] version of the internet. Already, it features applications and services that make use of blockchain technology. As such, it’s a community-owned and driven project. To date, there are more than 250 […]
[…] The company specializes in mining Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies at a large scale using blockchain technology. The company helps solve complex cryptographic algorithms with purpose-built […]
[…] The company specializes in mining Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies at a large scale using blockchain technology. The company helps solve complex cryptographic algorithms with purpose-built […]
[…] serve a function. As adoption soars, so will the worth of the tokens revolutionizing the affect of blockchain technology. If you wish to get in early, all you need to do is enter your electronic mail deal with within the […]
[…] additionally retains up in e-commerce, blockchain technology, and cell […]
[…] Changing technologies and new working methods have impacted jobs across the board and made it difficult for workers to keep up. Adapting to rapidly changing conditions is an ongoing challenge for workers across all industries. The roles and activities of workers will have to adapt to new conditions. […]
[…] Changing technologies and new working methods have impacted jobs across the board and made it difficult for workers to keep up. Adapting to rapidly changing conditions is an ongoing challenge for workers across all industries. The roles and activities of workers will have to adapt to new conditions. […]
[…] Changing technologies and new working methods have impacted jobs across the board and made it difficult for workers to keep up. Adapting to rapidly changing conditions is an ongoing challenge for workers across all industries. The roles and activities of workers will have to adapt to new conditions. […]
[…] new skills. And ongoing changes in the workplace could make the Udemy IPO an interesting prospect.Changing technologies and new working methods have impacted jobs across the board and made it difficult for workers to […]
[…] With a market cap round $65 billion, Cardano isn’t precisely a small fry within the crypto neighborhood. However this low cost crypto to purchase is at the moment buying and selling at near $2 a coin. So it’s actually on the low-cost facet of issues. However it’s additionally confirmed its means to face the check of time. It was launched in 2017. And it’s usually billed as a third-generation blockchain. […]
[…] With a market cap round $65 billion, Cardano isn’t precisely a small fry within the crypto group. However this low cost crypto to purchase is presently buying and selling at near $2 a coin. So it’s definitely on the low-cost facet of issues. Nevertheless it’s additionally confirmed its means to face the take a look at of time. It was launched in 2017. And it’s typically billed as a third-generation blockchain. […]
[…] With a market cap around $65 billion, Cardano isn’t exactly a small fry in the crypto community. But this cheap crypto to buy is currently trading at close to $2 a coin. So it’s certainly on the low-cost side of things. But it’s also proven its ability to stand the test of time. It was launched in 2017. And it’s often billed as a third-generation blockchain. […]
[…] new skills. And ongoing changes in the workplace could make the Udemy IPO an interesting prospect.Changing technologies and new working methods have impacted jobs across the board and made it difficult for workers to […]
[…] With a market cap round $65 billion, Cardano isn’t precisely a small fry within the crypto group. However this low-cost crypto to purchase is at present buying and selling at near $2 a coin. So it’s definitely on the low-cost facet of issues. However it’s additionally confirmed its potential to face the take a look at of time. It was launched in 2017. And it’s typically billed as a third-generation blockchain. […]
[…] and years. The other aspect we like is the pay-for-what-you-need model. Because this project is blockchain based, users own their data. And they only pay for what they want or […]
[…] and years. The other aspect we like is the pay-for-what-you-need model. Because this project is blockchain based, users own their data. And they only pay for what they want or […]
[…] and years. The other aspect we like is the pay-for-what-you-need model. Because this project is blockchain based, users own their data. And they only pay for what they want or […]
[…] and years. The other aspect we like is the pay-for-what-you-need model. Because this project is blockchain based, users own their data. And they only pay for what they want or […]
[…] and years. The other aspect we like is the pay-for-what-you-need model. Because this project is blockchain based, users own their data. And they only pay for what they want or […]
[…] and years. The other aspect we like is the pay-for-what-you-need model. Because this project is blockchain based, users own their data. And they only pay for what they want or […]
[…] The opposite facet we like is the pay-for-what-you-need mannequin. As a result of this venture is blockchain based mostly, customers personal their information. They usually solely pay for what they need or […]
[…] next-generation cryptos. These are the token poised to revolutionize the way we all interact with blockchain technology in the future. If you’d like to learn more, all you have to do is enter your email address in the […]
[…] next-generation cryptos. These are the token poised to revolutionize the way we all interact with blockchain technology in the future. If you’d like to learn more, all you have to do is enter your email address in the […]
[…] next-generation cryptos. These are the token poised to revolutionize the way we all interact with blockchain technology in the future. If you’d like to learn more, all you have to do is enter your email address in the […]
[…] With a market cap around $65 billion, Cardano isn’t exactly a small fry in the crypto community. But this cheap crypto to buy is currently trading at close to $2 a coin. So it’s certainly on the low-cost side of things. But it’s also proven its ability to stand the test of time. It was launched in 2017. And it’s often billed as a third-generation blockchain. […]
[…] is a cheap penny stock that could be a very smart move to make. It’s not a secret that many investors don’t understand blockchain, NFTs, […]
[…] is a cheap penny stock that could be a very smart move to make. It’s not a secret that many investors don’t understand blockchain, NFTs, […]
[…] action by updating and enhancing the scalability, transaction charges and affirmation delays in blockchain technology. At the start of 2021, it nonetheless appeared like a pie within the sky thought. However because […]
[…] action by updating and bettering the scalability, transaction charges and affirmation delays in blockchain technology. Originally of 2021, it nonetheless appeared like a pie within the sky thought. However because the […]
[…] to do so by updating and improving the scalability, transaction fees and confirmation delays in blockchain technology. At the beginning of 2021, it still seemed like a pie in the sky idea. But as the year progressed, […]
[…] to do so by updating and improving the scalability, transaction fees and confirmation delays in blockchain technology. At the beginning of 2021, it still seemed like a pie in the sky idea. But as the year progressed, […]
[…] to do so by updating and improving the scalability, transaction fees and confirmation delays in blockchain technology. At the beginning of 2021, it still seemed like a pie in the sky idea. But as the year progressed, […]
[…] to do so by updating and improving the scalability, transaction fees and confirmation delays in blockchain technology. At the beginning of 2021, it still seemed like a pie in the sky idea. But as the year progressed, […]
[…] to do so by updating and improving the scalability, transaction fees and confirmation delays in blockchain technology. At the beginning of 2021, it still seemed like a pie in the sky idea. But as the year progressed, […]
[…] to do so by updating and improving the scalability, transaction fees and confirmation delays in blockchain technology. At the beginning of 2021, it still seemed like a pie in the sky idea. But as the year progressed, […]
[…] action by updating and bettering the scalability, transaction charges and affirmation delays in blockchain technology. At the start of 2021, it nonetheless appeared like a pie within the sky thought. However because […]
[…] action by updating and enhancing the scalability, transaction charges and affirmation delays in blockchain technology. Firstly of 2021, it nonetheless appeared like a pie within the sky concept. However because the 12 […]
[…] to do so by updating and improving the scalability, transaction fees and confirmation delays in blockchain technology. At the beginning of 2021, it still seemed like a pie in the sky idea. But as the year progressed, […]
[…] They use travel, fintech and gaming to create unique advertising. They leverage the power of technology to create experiences and unique […]
[…] to do so by updating and improving the scalability, transaction fees and confirmation delays in blockchain technology. At the beginning of 2021, it still seemed like a pie in the sky idea. But as the year progressed, […]
[…] and “decentralized finance” (DeFi). These kind of video video games are constructed on blockchain technology. By pairing this with NFT ideas, GameFi permits gamers to be the only and verified house owners of […]
[…] of “gaming” and “decentralized finance” (DeFi). These types of video games are built on blockchain technology. By pairing this with NFT concepts, GameFi allows players to be the sole and verified owners of the […]
[…] of “gaming” and “decentralized finance” (DeFi). These types of video games are built on blockchain technology. By pairing this with NFT concepts, GameFi allows players to be the sole and verified owners of the […]
[…] of “gaming” and “decentralized finance” (DeFi). These types of video games are built on blockchain technology. By pairing this with NFT concepts, GameFi allows players to be the sole and verified owners of the […]
[…] of “gaming” and “decentralized finance” (DeFi). These types of video games are built on blockchain technology. By pairing this with NFT concepts, GameFi allows players to be the sole and verified owners of the […]
[…] and “decentralized financing” (DeFi). They are based on these types of video games blockchain technology. By pairing this with NFT GameFi allows players to be the sole and verified owners of the virtual […]
[…] of “gaming” and “decentralized finance” (DeFi). These types of video games are built on blockchain technology. By pairing this with NFT concepts, GameFi allows players to be the sole and verified owners of the […]
[…] of “gaming” and “decentralized finance” (DeFi). These types of video games are built on blockchain technology. By pairing this with NFT concepts, GameFi allows players to be the sole and verified owners of the […]
[…] of “gaming” and “decentralized finance” (DeFi). These types of video games are built on blockchain technology. By pairing this with NFT concepts, GameFi allows players to be the sole and verified owners of the […]
[…] of “gaming” and “decentralized finance” (DeFi). These types of video games are built on blockchain technology. By pairing this with NFT concepts, GameFi allows players to be the sole and verified owners of the […]
[…] some regularity. With just about every company you can think of trying to make some play into NFTs, blockchain technology or crypto, getting involved with the Shping Platform could be an easy point of entry for […]
[…] action by updating and enhancing the scalability, transaction charges and affirmation delays in blockchain technology. At the start of 2021, it nonetheless appeared like a pie in the sky thought. But because the yr […]
[…] some regularity. With just about every company you can think of trying to make some play into NFTs, blockchain technology or crypto, getting involved with the Shping Platform could be an easy point of entry for […]
[…] real tech behind Stacks crypto is its blockchain technology. It was designed to bring smart contracts and decentralized apps (DApps) to the Bitcoin blockchain. […]
[…] utilizing blockchain technology, Pawtocol crypto is looking to deliver valuable resources to animal shelters and rescues. And it […]
[…] utilizing blockchain technology, Pawtocol crypto is looking to deliver valuable resources to animal shelters and rescues. And it […]
[…] similar to the traditional SWIFT payment network. However, the company sets itself apart by using blockchain technology to improve transparency and security. With Ripple’s global blockchain-based real-time financial […]
[…] similar to the traditional SWIFT payment network. However, the company sets itself apart by using blockchain technology to improve transparency and security. With Ripple’s global blockchain-based real-time financial […]
[…] similar to the traditional SWIFT payment network. However, the company sets itself apart by using blockchain technology to improve transparency and security. With Ripple’s global blockchain-based real-time financial […]
[…] similar to the traditional SWIFT payment network. However, the company sets itself apart by using blockchain technology to improve transparency and security. With Ripple’s global blockchain-based real-time financial […]
[…] similar to the traditional SWIFT payment network. However, the company sets itself apart by using blockchain technology to improve transparency and security. With Ripple’s global blockchain-based real-time financial […]
[…] is a blockchain-focused financial service company. Since its inception in 2013, the company built products designed to help […]
[…] is a blockchain-focused financial service company. Since its inception in 2013, the company built products designed to help […]
[…] is a blockchain-focused financial service company. Since its inception in 2013, the company built products designed to help […]
[…] fintech and gaming to create unique advertising. In addition, the company leverages the power of technology to create experiences and unique […]
[…] of “gaming” and “decentralized finance” (DeFi). These types of video games are built on blockchain technology. By pairing this with NFT concepts, GameFi allows players to be the sole and verified owners of the […]
[…] blockchain technology can be used by institutions, governments and even private enterprises. Its decentralization, […]
[…] blockchain technology can be used by institutions, governments and even private enterprises. Its decentralization, […]
[…] blockchain technology can be used by institutions, governments and even private enterprises. Its decentralization, […]
[…] present measurement, the PolySwarm crypto mission has oversized objectives. Specifically, making blockchain era more secure and freed from disruptive malware. And it’s set out to take action via using a suave […]
[…] is the future of the company. So much so, in fact, that he rebranded the company after blockchain. Blockchain is the technology that powers Bitcoin. If you believe that Bitcoin is the future then go ahead and […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] make clear, oracles exist to attach blockchains to exterior programs. This helps blockchain technology operate in actual world functions. They allow sensible contracts to be executed based mostly on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] make clear, oracles exist to attach blockchains to exterior methods. This helps blockchain technology perform in actual world purposes. They allow sensible contracts to be executed primarily based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] clarify, oracles exist to connect blockchains to external systems. This helps blockchain technology function in real world applications. They enable smart contracts to be executed based on […]
[…] next-generation cryptos. These are the token poised to revolutionize the way we all interact with blockchain technology in the future. If you’d like to learn more, all you have to do is enter your email address in the […]
[…] is a blockchain-focused financial service company. Since its inception in 2013, the company built products designed to […]
“Kickstart Your Fiverr Freelancing Journey: 1hr 10min Video & Audio Course – https://mazkingin.com/complete-basics-to-fiverr-freelancing/“
Passive Income with ChatGPT: Lucrative Ideas to Earn Money While You Sleep : https://mazkingin.com/passive-income-with-chatgpt-lucrative-ideas-to-earn-money-while-you-sleep/
I really like your writing style. It’s very engaging and easy to follow. How to Become a Top Rated Seller on Fiverr.com : https://mazkingin.com/how-to-become-a-top-rated-seller-on-fiverr-com/
This is fantastic! Please continue with this great work. By the way, we are excited to announce a $3,000 giveaway program. Simply share the post on Facebook for a chance to win $3,000. Visit: https://jivoice.com/giveaway/
how to earn money with amazon kindle – A total guide video training – : https://mazkingin.com/how-to-earn-money-with-amazon-kindle/
This blog is like a virtual mentor, guiding me towards personal and professional growth Thank you for being a source of inspiration
Earn Money by Copywriting : Make Money by CopyWriting From Home – Video training guide – : https://mazkingin.com/earn-money-by-copywriting-make-money-by-copywriting-from-home/
Passive Income – 35+ Tools/Websites to Earn Money – Video training guide. Download from GoogleDrive – : https://mazkingin.com/passive-income-35-tools-websites-to-earn-money/
Make your bitcoin work for you with daily profits and up to 25% returns. Invest in this Islamic Shariya Halal opportunity now! https://investurns.com/
Learn Stock Market Trading | Earn Money | Practical Training – Video training guide. Download from GoogleDrive – : hhttps://mazkingin.com/learn-stock-market-trading-earn-money-practical-training/
The topics covered here are always so interesting and unique Thank you for keeping me informed and entertained!
Join https://investurns.com/ and enjoy daily profits and repayments. Earn up to 25% returns on your investment.
I have been struggling with this issue for a while and your post has provided me with much-needed guidance and clarity Thank you so much
Looking for a Halal investment opportunity? Earn up to 25% profit daily at https://investurns.com/.
Your blog is always full of useful information, thanks for this post! Share the post on Facebook and WIN 3000USD. Visit: https://giveaway.jivoice.com
This is a great article! It’s packed with information and written in a clear and engaging style. I’ll definitely be coming back to read more from your blog. https://nftbeyond.com/
Goal Setting for Happiness and Success – Download video training – https://mazkingin.com/goal-setting-for-happiness-and-success/
Motivational Milestones: Top 10 Quotes to Ignite Your Spirit : https://jivoice.com/motivational-milestones-top-10-quotes-to-ignite-your-spirit/
Cryptocurrency Arbitrage Earn Money everyday Easy – Download Video Training – https://mazkingin.com/cryptocurrency-arbitrage-earn-money-everyday-easy/